Continuous Raster Data Examples
One of the best things that I like about D3 is the ridiculous amount of awesome demos available online and last night I have stumbled on an excel sheet with 1134 examples of data visualizations with D3. An example of discrete raster data is population density.

What Is Raster Data Help Documentation
Oil depth across an open-water oil spill soil pH.

. Surface interpolation tools make predictions from sample measurements for all locations in an output raster dataset whether or not a measurement has been taken at. Lets start with the basics. The scatterplot is a very important tool for assessing the relationship between two continuous variables.
For example you can add values of NUMBER data type but not values of RAW data type. Each cell has a value that represents information. A feature is anything you can see on the landscape.
Raster TIN terrain dataset and LAS datasets are all types of a functional surface. Percent tree cover percent non-tree cover and percent non-vegetated bare. To create a simple world map we need to specify the data object world_moll inside the tm_shape function and the way we want to visualize itThe tmap package offers several visualisation possibilities for polygons including tm_borders tm_fill and tm_polygonsThe last one draws the filled polygons with borders.
What is Raster Data. Each cell has a value representing a property or attribute of interest. The next issue is vector to raster and raster to vector conversion which is often occurs in spatial analysis with two data types.
Here is an update with over 2000 D3js examples. The host computer is responsible for sending commands and data to the printer to form each individual raster line of data. The original raster data of 4m by 4m resolution from hyperspectral images.
Continuous and Discrete Raster Data. 83 Very large data cubes. Vector data is the representation of spatial features in points lines polygon formats and it is a discrete data representation.
Besides this it follows international technical standards for different software component interactions. A grid of cells represents this data. In other words it is a matrix of cells organized into rows and columns.
The following code uses functions introduced in a later section. Data Infrastructure as a Service IaaS. Each value manipulated by Oracle Database has a data type.
The continuous surface representation of a raster dataset represents some measure such as the height concentration or magnitude for example elevation acidity or noise level. These properties cause Oracle to treat values of one data type differently from values of another. Raster data is.
Some data generation processes are continuous in space and may be observed everywhere. Note that using gsn_csm_contour results in the raster bins at the edges being reduced to half width. Come back to this after reading section 752 which introduces methods for plotting two.
Some simple examples of 3D surfaces are a landscape an urban corridor gas deposits under the earth and a network of well depths to determine water table depth. This is generally performed by printer drivers in the host computer that convert the image of the label into the proper command and data stream required by the printers. Validation at stage 3 has been achieved for the MODIS Vegetation Continuous Fields data.
It is converted to 30m by 30m resolution using center value aggregation. 328Each one of these things would be a feature when we represent them in a GIS. 9 Plotting spatial data.
75 raster-to-vector vector-to. Raster data is cell-based and this data category also includes aerial and satellite imagery. Looking down you can see houses roads trees rivers and so on see Fig.
The continuous surface representation of a raster dataset represents some measure such as the height concentration or magnitude for example elevation acidity or noise level. The figure is land cover map of before and after spatial aggregation. These clearly show the bin and data resolution.
Surface interpolation tools make predictions from sample measurements for all locations in an output raster dataset whether or not a measurement has been taken at. 51 Revealing uncertainty If you have information about the uncertainty present in your data whether it be from a model or from distributional assumptions its a good idea to display it. While any type of geographic data can be stored in raster format raster datasets are especially suited to the representation of continuous rather than discrete data.
This data model often refers to so-called regular grids in which each cell has the same constant size. For example OGC and ISO are for delivering maps vectors and raster data. Variables that may not be continuous probabilities00 may be best viewed via use of raster plots.
74 Vector data cube examples. There are two types of raster data. Imagine you are standing on the top of a hill.
Chemical concentrations and elevation surface are some examples of raster data. In the GIS world there are two primary data formats one is a vector and another one is raster data formats. The data type of a value associates a fixed set of properties with the value.
Some examples of continuous data are. The MOD44B Version 6 Vegetation Continuous Fields VCF yearly product is a global representation of surface vegetation cover as gradations of three ground cover components. These are all examples of real features but surfaces could be derived or imaginary.
However when the data is large points will. Vector data provide a way to represent real world features within the GIS environment. If the roll has continuous form paper the Form.
Each pixel has an associated value. In computer graphics and digital photography a raster graphic represents a two-dimensional picture as a rectangular matrix or grid of square pixels viewable via a computer display paper or other display mediumA raster is technically characterized by the width and height of the image in pixels and by the number of bits per pixelRaster images are stored in image files with varying. The spatial raster data model represents the world with the continuous grid of cells often also called pixels.
A simple scatter plot does not show how many observations there are for each x y valueAs such scatterplots work best for plotting a continuous x and a continuous y variable and when all x y values are uniqueWarning. Others are discrete observed in tesselated. Raster data is a representation of images in rows and columns of pixel format and it is a continuous data representation.
Spatial Data Repository for storage of data. 92 Plotting points. GIS software for creation and upgradation purpose of Spatial Data.
91 Every plot is a projection. Continuous data examples are temperature and elevation measurements. Raster data consists of pixels.

Building Models For Gis Analysis Using Arcgis Analysis Remote Sensing Model
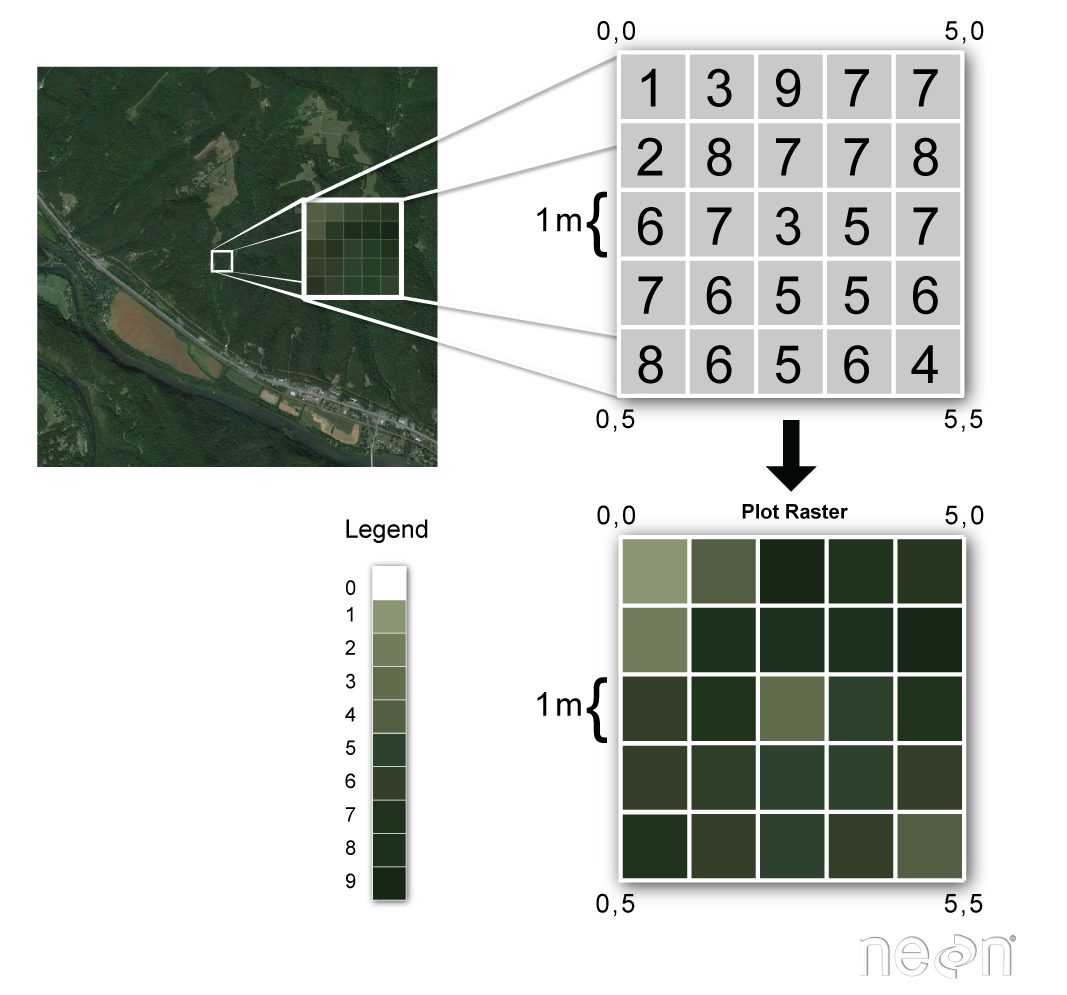
Introduction To Raster Data Introduction To Geospatial Concepts
Discrete And Continuous Data Arcmap Documentation

Introduction To Raster Data Introduction To Geospatial Concepts
No comments for "Continuous Raster Data Examples"
Post a Comment